Thermal power is efficient heat and power production
Our five thermal power plants are combined heat and power plants. They produce process steam for industries, as well as district heat for communities. In addition, they produce electricity.
Almost a third of all the electricity produced in Finland is generated in combined heat and power plants. At best, up to 90% of the energy in fuel can be converted into heat and electricity in this way.
In 2024, the heat output of the combined heat and power plants was 2.5 TWh, and the electricity output was 0.7 TWh. We have no separate production plants, i.e. condensing power plants, for electricity production.
Wood-based fuels as primary fuels
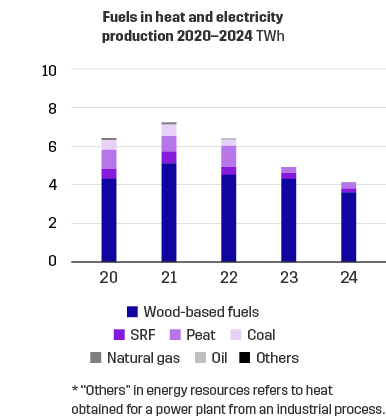
The use of fuels depends on energy production. Our combined heat and power plants primarily use by-products from forestry, wood-based fuels, as their fuel. Peat, SRF and coal are also used. Oil and natural gas are used as start-up and backup fuels.
The wood-based fuels in our combined heat and power plants are sustainably sourced. Our goal is to restrict the use of fossil fuels, including peat, to start-up and backup fuels alone by 2025 – if the market allows this. We are determined to advance towards CO2 neutrality.
Read more about how this is done in the Responsibility section.
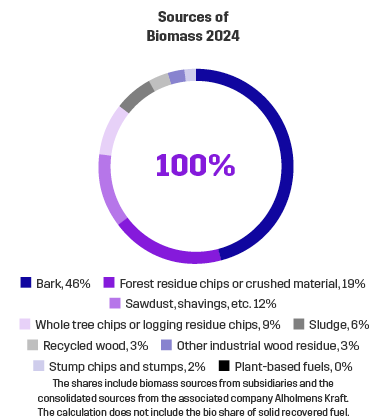
We are one of Finland’s leading users of solid biofuels.
Recycled fuel (Solid Recovered Fuel, SRF) is fuel produced from waste. It usually contains energy waste that is unsuitable for material re-usage, such as soiled carton or paper.
We promote circular economy at a few of our power plants by using the heat and by-products generated in industrial processes as our energy sources. They replace some of the fuels used by the power plants in the production of energy.
Emissions from thermal power decreasing
The most significant environmental impact of thermal power production concerns the atmosphere. All Pohjolan Voima’s power plants have environmental permits in force. Our thermal power plants have greenhouse gas emission permits and allowances related to the EUA emission allowance trade.
The CO2 emissions have been on the decrease, mainly due to the fact that less coal is used. In 2024, carbon dioxide emissions from the production of electricity and heat amounted to 0.2 million tonnes.
Emissions into the air declined somewhat from the previous year, except for nitrogen oxides. Sulphur dioxide emissions amounted to 0.2 thousand tonnes, nitrogen oxide emissions to 1.0 thousand tonnes and particle emissions to 0.05 thousand tonnes.
See also in the Responsibility section how we reduce emissions further
Increased flexibility with development projects
To achieve our strategic goals, we have initiated a host of development projects involving CO2-neutrality, regulation capability and management of the production assets.
We seek innovative solutions and aim to
- further reduce emissions
- improve the reliability of production
- enhance efficiency
- become more flexible
- achieve lower lifecycle costs.
We are searching for means to further improve the utilisation of fuels at our combined heat and power plants so that we could only use peat and fossil fuels as startup and backup fuels whenever the market situation allows.
We develop the regulation capability of our operations and improve our lifecycle cost management and production processes. We also consider the circulation economy goals in our projects. Read more about promoting the circular economy in the Responsibility section.
In the development work, we utilise new opportunities offered by digitalisation and knowledge-based management. We invest in smart systems and low threshold pilot projects that we implement in cooperation with our partner networks.